For almost all of human history, food was scarce for nearly everyone. The reason for this perpetual scarcity was that whenever food production increased, it did not lead to more food per capita but to more people.
Food production did not increase per capita. Population pressure ensured that living standards remained only barely above the subsistence level. Economic historians refer to this mechanism as the Malthusian Trap, and if you'd like to know more, you could read my article about it.
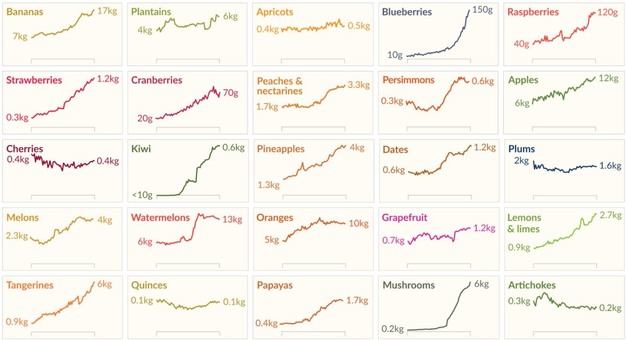
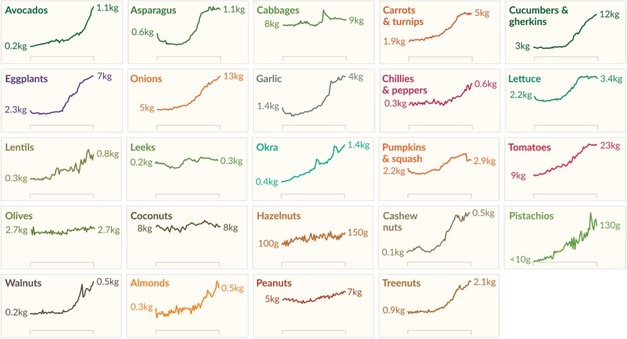
This changed in the last decades. More and more societies around the world broke out of the Malthusian Trap. We see this in the data as increasing food production in per capita terms. The chart shows that farmers have grown many fruits, vegetables, and nuts faster than the world population has increased.
The increase in global agricultural output was crucial for the reduction of hunger and famines that the world achieved in this period. Whether or not we will be able to end hunger globally will depend on whether this increase in food production will continue.
For more information:
Our world in data
Email: [email protected]
www.ourworldindata.org